
Calculate & draw the positions of the Galilean satellites
galsat.Rdgalsat() is used to determine the positions of the four greatest satellites
of Jupiter (called Galilean satellites). Positions are shown on the plot for
given UTC time (Coordinated Universal Time between year 0 and 3000) with respect
to the planet, as seen from the Earth.
The galsat() function returns numerical values of the satellites' positions:
x - the apparent rectangular coordinate of the satellite with respect to the center of Jupiter's disk in the equatorial plane in the units of Jupiter's equatorial radius; X is positive toward the west
y - the apparent rectangular coordinate of the satellite with respect to the center of Jupiter's disk from the equatorial plane in the units of Jupiter's equatorial radius; Y is positive toward the north
u_corrected - the corrected angular position of the satellite in degrees, used to determine visibility conditions (whether a moon can be seen against Jupiter's disk or is hidden behind it)
Value
data.frame: 4 observations of 4 variables:
$ moon : chr "Io" "Europa" "Ganymede" "Callisto"
$ x : num
$ y : num
$ u_corrected: num
Four rows - each row has the position (x,y) and corrected angular position (u_corrected) of one moon.
Additionally, the positions of the moons are shown graphically.
Details
The function is based on algorithms in the book: Astronomical Formulae for Calculators (4th edition), Jean Meeus, Willmann-Bell Inc., 1988
Examples
galsat(2025, 10, 13, 23, 30)
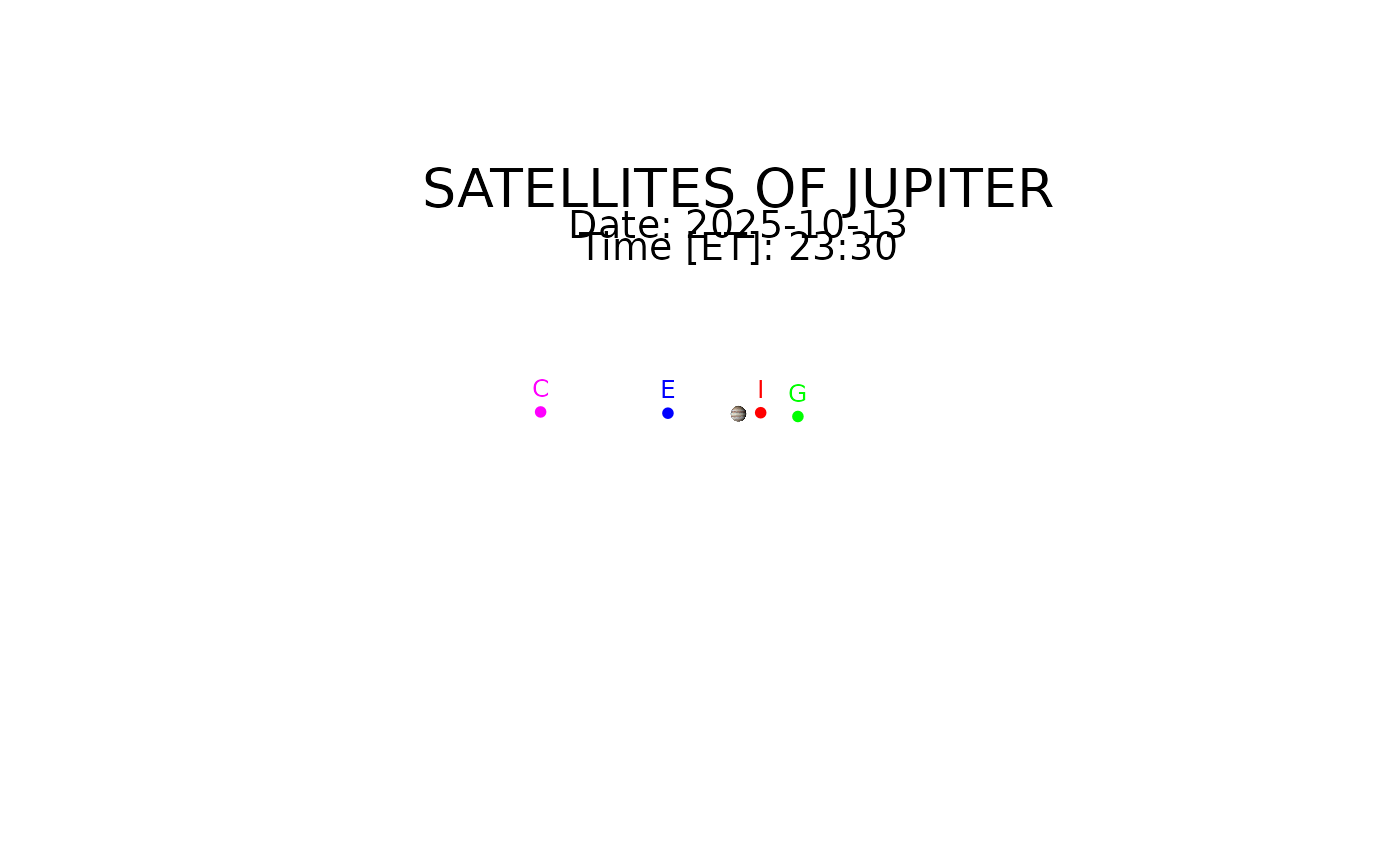 #> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 2.802832 0.1370436 151.7898
#> 2 Europa -8.908685 0.0772815 251.6987
#> 3 Ganymede 7.529880 -0.3393067 30.2019
#> 4 Callisto -24.999085 0.2351669 250.2692
# Also try these interesting configuration moments:
galsat(2021, 8, 15, 15, 48)
#> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 2.802832 0.1370436 151.7898
#> 2 Europa -8.908685 0.0772815 251.6987
#> 3 Ganymede 7.529880 -0.3393067 30.2019
#> 4 Callisto -24.999085 0.2351669 250.2692
# Also try these interesting configuration moments:
galsat(2021, 8, 15, 15, 48)
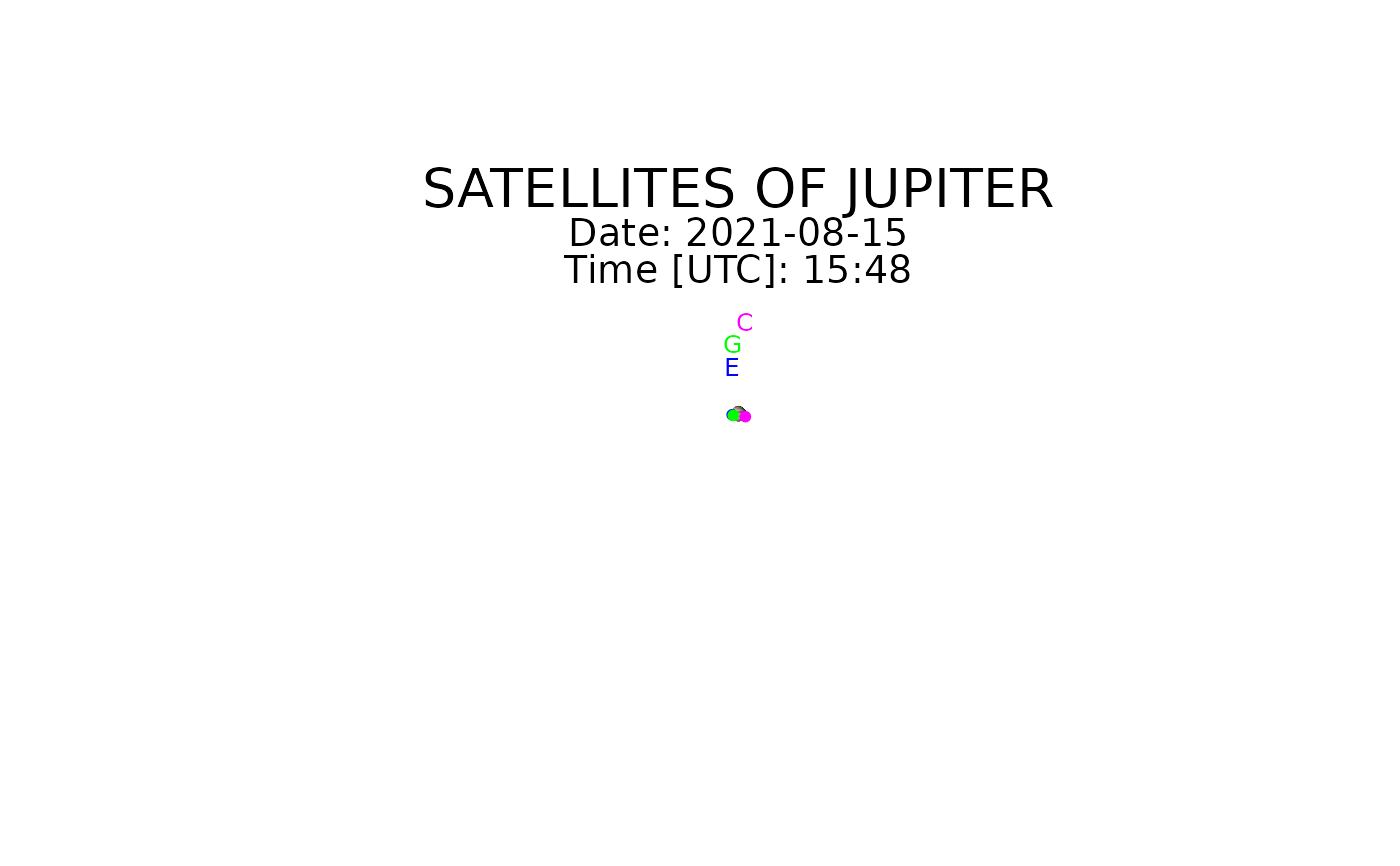 #> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 0.9797847 0.07917838 170.411403
#> 2 Europa -0.7906981 -0.12661976 355.127268
#> 3 Ganymede -0.6605975 -0.20468771 357.477237
#> 4 Callisto 0.8873500 -0.36182567 1.917545
galsat(2032, 1, 5, 6, 44)
#> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 0.9797847 0.07917838 170.411403
#> 2 Europa -0.7906981 -0.12661976 355.127268
#> 3 Ganymede -0.6605975 -0.20468771 357.477237
#> 4 Callisto 0.8873500 -0.36182567 1.917545
galsat(2032, 1, 5, 6, 44)
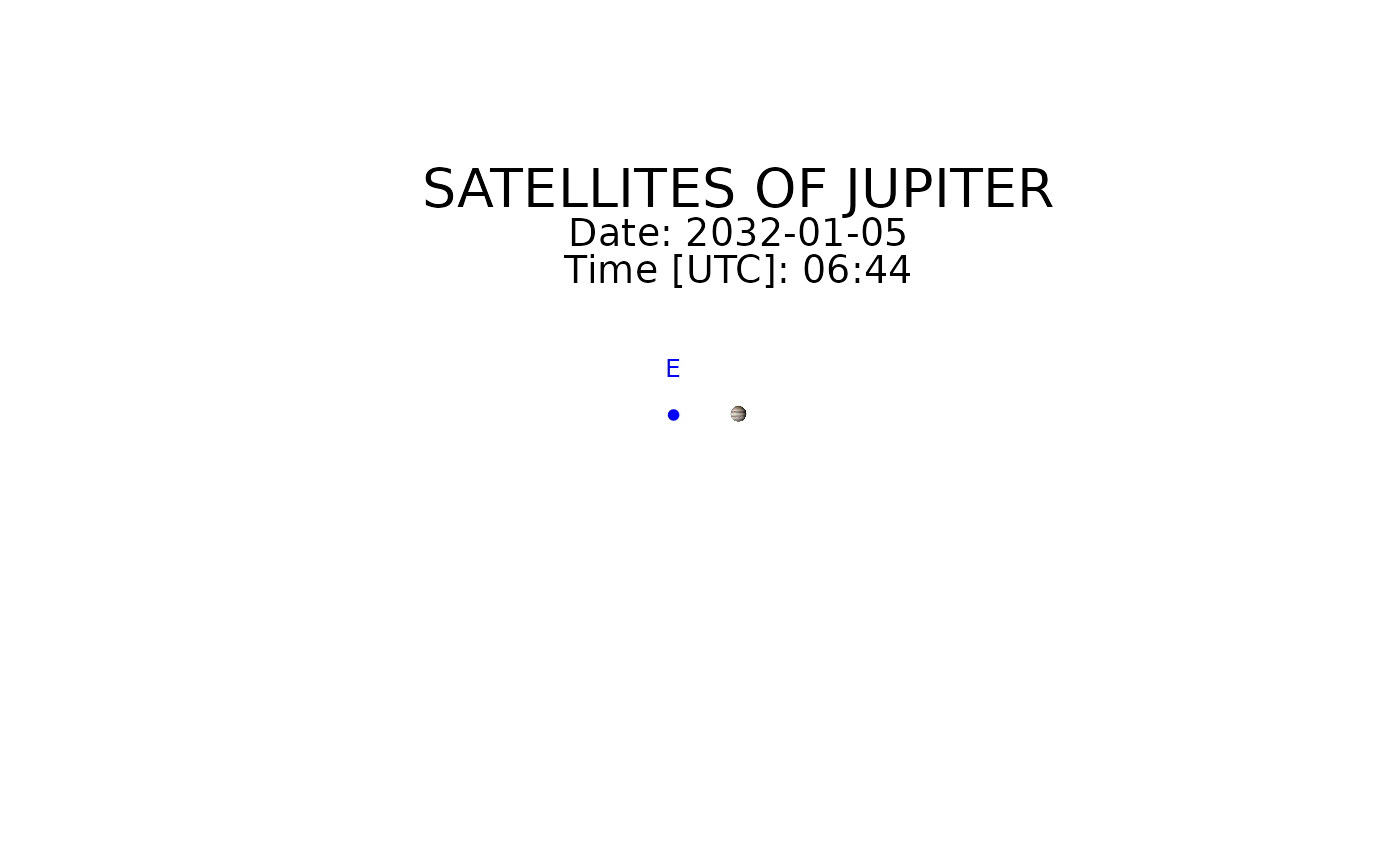 #> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 0.22409172 -0.1877863 177.8303
#> 2 Europa -8.19592931 -0.1487233 240.2495
#> 3 Ganymede 0.06620236 -0.4752985 179.7466
#> 4 Callisto -0.43339665 -0.8370223 180.9418
galsat(2033, 7, 28, 4, 50)
#> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 0.22409172 -0.1877863 177.8303
#> 2 Europa -8.19592931 -0.1487233 240.2495
#> 3 Ganymede 0.06620236 -0.4752985 179.7466
#> 4 Callisto -0.43339665 -0.8370223 180.9418
galsat(2033, 7, 28, 4, 50)
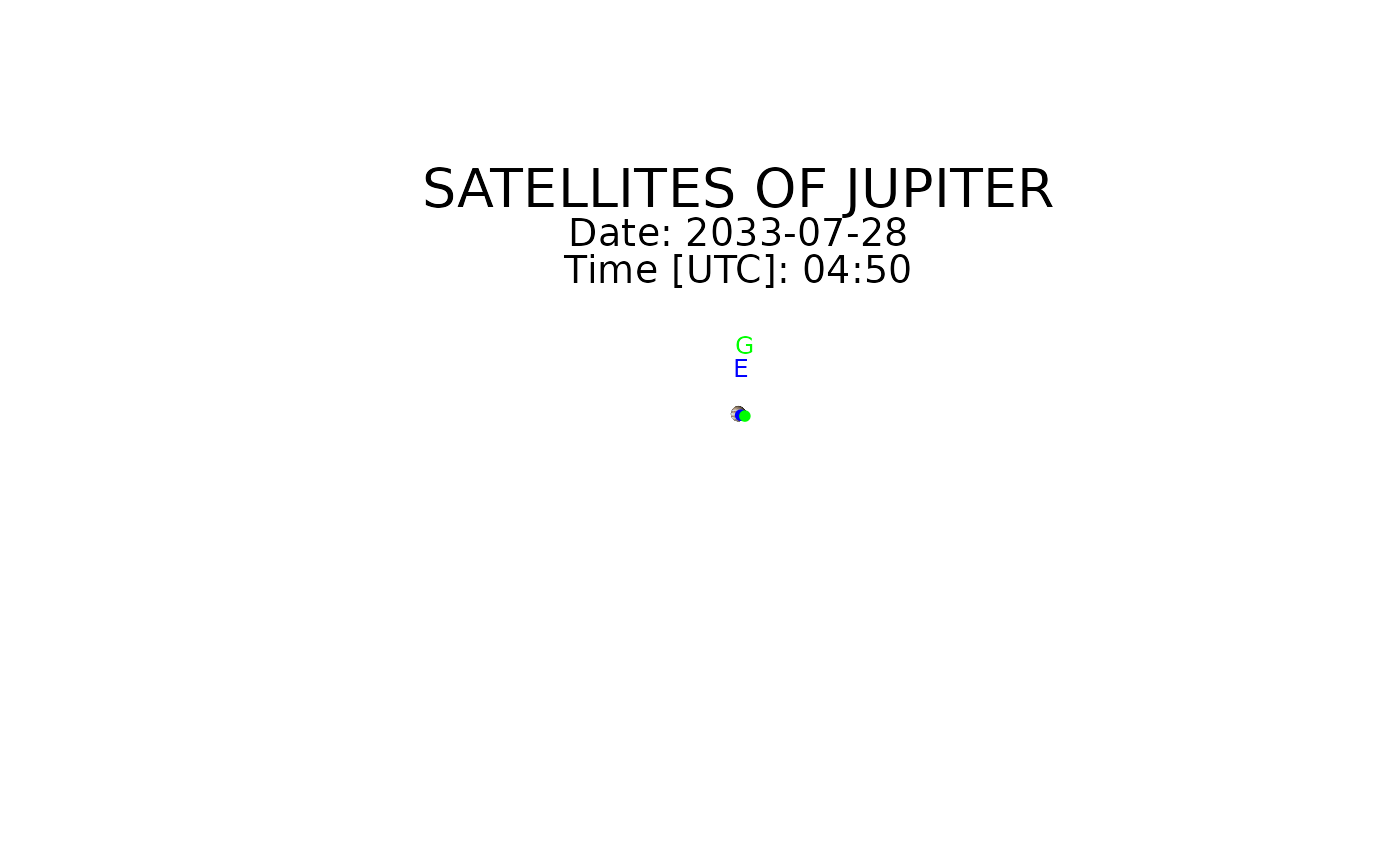 #> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 0.1130089 0.1120284 178.899094
#> 2 Europa 0.2794994 -0.1772460 1.720653
#> 3 Ganymede 0.8199864 -0.2855337 3.131382
#> 4 Callisto -0.4619301 0.4992523 181.009789
galsat(2039, 7, 31, 18, 55)
#> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 0.1130089 0.1120284 178.899094
#> 2 Europa 0.2794994 -0.1772460 1.720653
#> 3 Ganymede 0.8199864 -0.2855337 3.131382
#> 4 Callisto -0.4619301 0.4992523 181.009789
galsat(2039, 7, 31, 18, 55)
 #> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 0.8650198 -0.0821923525 171.54352
#> 2 Europa 0.4450186 -0.1338542538 177.31099
#> 3 Ganymede 14.9887339 -0.0006076166 90.16442
#> 4 Callisto -1.1553599 -0.3741162112 182.49804
#> moon x y u_corrected
#> 1 Io 0.8650198 -0.0821923525 171.54352
#> 2 Europa 0.4450186 -0.1338542538 177.31099
#> 3 Ganymede 14.9887339 -0.0006076166 90.16442
#> 4 Callisto -1.1553599 -0.3741162112 182.49804